PACS vs. VNA
You've probably noticed the growing imaging data in your healthcare environment. Each scan adds more information to store and make accessible across systems and departments, all while supporting clinical workflows. If current use patterns continue, imaging volumes could range from 5.6% lower to 45.2% higher by 2030, with population growth accounting for most of this increase.
As demand grows, your team faces two distinct pressures. Radiologists prioritize speed and reliability because timely access to imaging influences diagnoses and patient care. Meanwhile, IT leaders focus on interoperability, secure long-term storage and seamless access across facilities, ensuring information flows where it's needed.
Picture archiving and communication system (PACS) and vendor-neutral archive (VNA) can balance these priorities. These medical imaging technologies inform the imaging infrastructure, and though they originate from different architectural philosophies, they can support your unique needs.
Explore what PACS and VNA are, along with their functions and differences.
What Is PACS?
PACS is a clinical imaging solution that stores and manages medical images in radiology departments. It enables you to quickly access, retrieve and integrate digital workflows.
PACS features various functions, including:
- Centralized secure storage: When you capture an imaging study, whether it's an MRI, CT, ultrasound or plain X-ray, it lands in PACS almost immediately. PACS stores these images securely until they're ready for retrieval. The storage layer handles high throughput, so when clinicians request studies, the system delivers them quickly.
- Digital image acquisition: PACS connects directly to modalities using standard protocols, like the Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) standard. This means that as soon as a scanner generates an image, it's pushed into PACS with associated metadata. This linkage between creation and storage reduces manual steps on your end and ensures images flow efficiently from acquisition to the clinical view.
- Instant retrieval and access: One reason PACS is invaluable in radiology is its speed. When you or your team click to open a prior study, PACS delivers it with minimal delay. This immediacy allows you to compare studies side by side or collaborate across shifts.
- Image distribution and routing: PACS routes images to the right viewers and workstations. It can send relevant studies to referring systems and enable access for multidisciplinary teams, which helps your clinical users stay connected.
What Is a VNA in Healthcare?
VNA in healthcare is an enterprise-oriented architecture that stores and manages medical images independently of any single viewing application or departmental system. It refers to an archive that decouples image storage from the systems you use to view or interpret images, giving you greater control over imaging data across departments and vendors.
VNA functions support various imaging strategies, including:
- Centralized imaging repository: A VNA serves as a single source of truth for imaging data across the organization. It consolidates images into a unified repository, reducing data fragmentation and ensuring consistent storage and access.
- Interoperability and standardized access: VNAs use standardized formats and interfaces to help you consistently access images across systems and vendors. This standardization reduces reliance on proprietary data structures and minimizes barriers to data sharing.
- Support for diverse file types: A VNA accommodates a range of imaging and multimedia content, including cardiology images and other non-DICOM formats.
- Long-term archive and data life cycle management: VNAs support long-term image retention. They support data life cycle policies that manage how you store and retain images, which helps you balance performance and compliance as imaging volumes grow.
The Difference Between PACS and VNA
Teams may use PACS and VNA interchangeably, but they address distinct layers of the imaging ecosystem. Knowing how each handles data can help you decide which system best fits your needs.
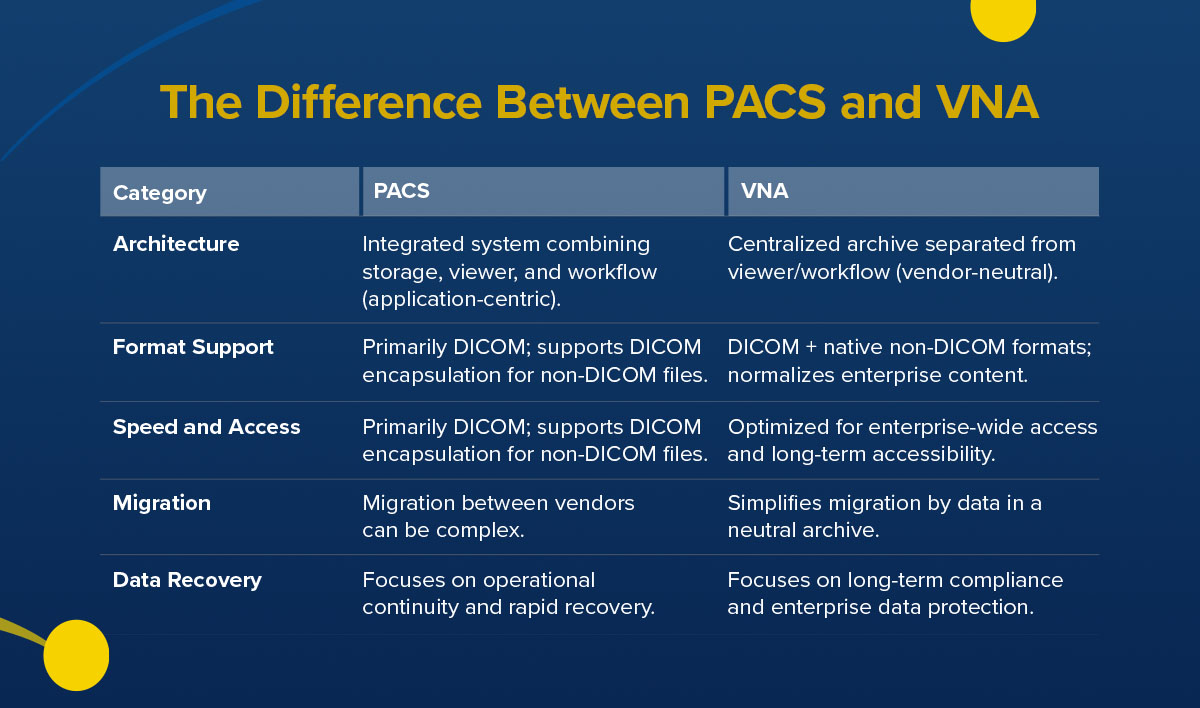
1. Architecture
One difference between PACS and VNA is how they store data. PACS is application-centric because it combines image storage, diagnostic viewers and workflow tools into a tightly integrated platform to support your interpretation of radiology data. This enables usability and seamless workflow integration, helping radiologists move through high-volume cases efficiently. Some PACS platforms also feature intelligent parsing and routing and enterprise-level storage, allowing for enterprise-wide data management.
VNA separates storage from workflow and viewing applications, creating a centralized archive you can access via multiple systems and departments. This approach supports long-term flexibility, letting you integrate new imaging modalities or expand across sites.
2. Format Support
PACS platforms support the DICOM standard. This focus allows the system to optimize performance for complex imaging studies, like CT and MRI, where image fidelity and presentation consistency support interpretation quality.
PACS also features DICOM encapsulation. This allows non-DICOM content to be attached to imaging studies and preserves these files within a DICOM framework, which keeps your clinical content linked to a diagnostic exam.
VNAs take a broader approach to format support. In addition to DICOM images, they store and normalize a wide range of native non-DICOM content across specialties. This design supports enterprise imaging strategies, helping maintain consistency and accessibility across departments.
3. Speed and Access
Speed is a hallmark of PACS. Prefetching and optimized retrieval allow you to access studies instantly, which supports high-volume reading sessions and time-sensitive interpretation. PACS also supports distributed access, bridging the speed of integration with cross-departmental availability.
VNA access emphasizes breadth and continuity. It balances peak performance with enterprise-wide accessibility and ensures clinicians across departments can retrieve imaging reliably.
4. Migration
PACS upgrades or replacements can involve moving data between vendor-specific systems, which requires careful planning to maintain clinical continuity. These solutions incorporate long-term archiving and smart data routing, allowing you to transition smoothly between vendors or hybrid workflows that require clinical speed and enterprise continuity.
VNAs simplify migration by acting as a vendor-neutral repository. Images remain in place while front-end PACS applications change, reducing complexity and operational risk.
5. Data Recovery
PACS prioritizes operational continuity by restoring access to ensure you maintain workflow momentum. The system integrates disaster recovery and scalable storage features, providing immediate operational support and secure long-term preservation.
VNAs support regulatory compliance and enterprise-wide recovery, helping protect your institutional knowledge over the years.

Find Reliable PACS Solutions From Candelis
When you're looking for a PACS solution that fits your operational needs, you want something that's intuitive to use and keeps imaging flowing across your organization. Candelis offers a wide range of PACS options under the ImageGrid™ platform. The ImageGrid™ PACS server is an affordable, feature-rich system that works well in small and large imaging centers. It combines robust image archiving with intelligent routing and flexible storage.
For clinics and hospitals seeking a compact system, the ImageGrid™ Mini PACS server delivers essential capabilities at a cost-effective price. It comes with built-in storage and a diagnostic viewer. If your environment is virtualized, our ImageGrid™ VM features enterprise-grade capabilities in a ready-to-deploy virtual appliance. It works with VMware and features scalable local storage, so you can optimize resources dynamically.
For organizations that favor a cloud-first strategy, ImageGrid™ Cloud PACS gives you the benefits of a full system without requiring on-premises hardware. It includes advanced routing, multimodality support and integration with third-party systems.
Across the ImageGrid™ family, you'll find seamless integration, scalable storage and tools built for your specific workflows. Setups and administration are straightforward, letting your team focus on interpreting and using imaging data.
Contact us today to learn more.
- Log in to post comments
