What Are the 4 Major Components of PACS?
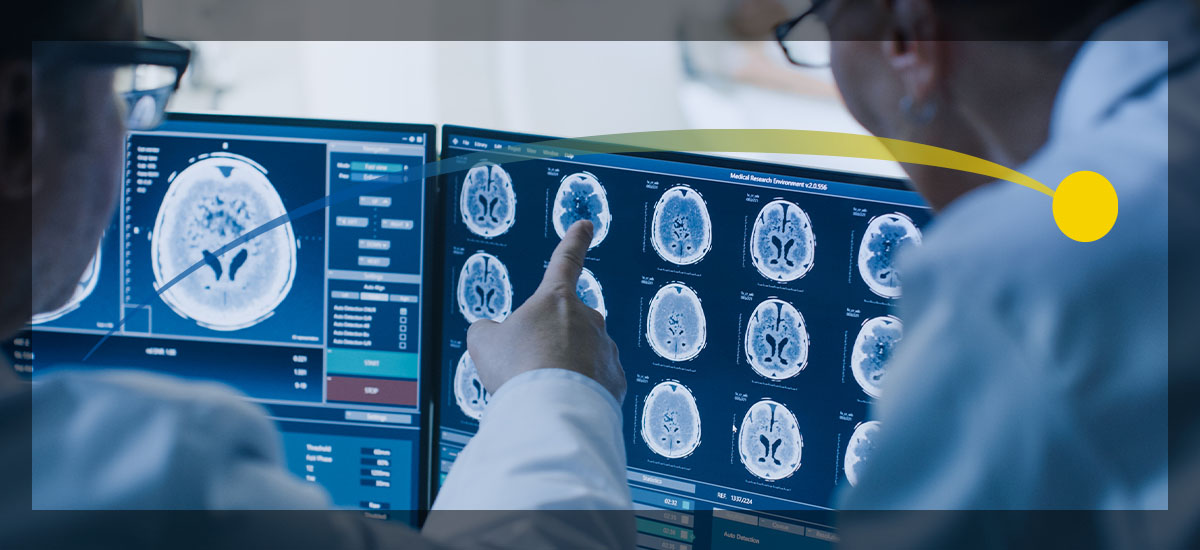
In the health care industry, picture archiving and communication system (PACS) facilitate the easy access, retrieval and storage of film-based information. Digital imaging technology optimizes key processes in managing patient information through enhanced viewing and analysis. It’s essential to understand the four main components of PACS and how each contributes to workflow improvement and patient satisfaction.
Component 1: Image Acquisition Devices
The first key element of PACS includes the imaging acquisition devices used to scan the patient and the acquisition gateway computers that produce the medical images.
Some of the most common imaging acquisition modalities include:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Positron emission tomography (PET)
- Computed tomography (CT)
- X-ray
- Angiography
The imaging modality connects to a gateway computer. Through the PACS server, the gateway computer obtains relevant medical images from the modality and converts them into the standard PACS format. Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) is the universal PACS format that enables image resizing and orientation calibration of medical data.
Component 2: Secure Networks for Transmission
PACS relies on a secure communication network for the safe, seamless transmission of medical data. The PACS network curates a specific path for moving key information between other PACS components, relevant departments and even remote locations.
The key network types used in the transfer of medical data include:
- LAN networks within a department: This type of network links to a specific department’s imaging modalities, display workstations and archive.
- LAN networks that connect to various departments: This type of network covers intrahospital transmission of data.
- Teleradiology networks: This type of network repositions medical information between hospitals.
To ensure a secure network for the acquisition, distribution and exchange of medical images, PACS networks must consider three main factors — network topology, workflow assignments and line capacity. The topology of a PACS network varies depending on the existing network architectural type.
Component 3: Workstations or Viewing Stations
A workstation is one of the main PACS components, allowing radiologists and clinicians to review images and patient information. Workstations provide the detailed view of medical data specialists need to create a primary diagnosis.
A modern display workstation has communication hardware, processing software, a display monitor system, a local database and resource management. Workstations offer a range of image-processing capabilities, including:
- Access
- Processing
- Manipulation
- Interpretation
- Evaluation
- Documentation
Display workstations vary in resolution. Radiology departments generally use high-resolution LCDs for primary diagnosis, while hospital wards rely on medium-resolution LCDs for primary diagnosis of sectional medical images.
Component 4: Servers and Storage
The storage and retrieval of medical records are crucial in PACS. A PACS server is a centralized computing device that stores image modalities from the acquisition devices using a DICOM viewer.
As the cornerstone of PACS, the server needs a storage media and archive system. The archive system requires two levels for the retrieval of medical data — short-term and long-term.
Various types of storage architecture exist within PACS servers:
- Storage area network (SAN): Corporate data centers widely capitalize on this type of network because of its dedicated server storage. It's an independent network that connects storage devices to computers.
- Network-attached storage (NAS): This type of network also offers independent server storage, though it differs from SAN in attachment. NAS sits on the network, so network standard protocols are necessary to access the storage.
- Direct-attached storage (DAS): Hard drives on the server that runs the PACS can also store records. While this is a simple and direct approach to storage, scalability is limited.
Key Benefits of PACS in the Health Care Industry
PACS offers a myriad of perks to the health care industry and patient care. Some of the benefits of PACS for hospitals, health care equipment providers and imaging centers include:
- Eliminating the manual process of filing, storage, retrieval and transfer of medical data.
- Ensuring the secure transmission of sensitive medical information.
- Offering seamless transfer and access of data from on-site and off-site networks.
- Streamlining relevant hospital internal processes, including testing, billing and discharge.
- Providing access to the most updated version of medical images and clinical reports.
- Helping clinicians, radiologists and PACS administrators with their workflows.
- Improving diagnosis processes, quality of care and overall patient satisfaction.
Leverage Fully Featured PACS From Candelis for Optimized Workflow
Candelis offers an end-to-end PACS solution for seamless medical image management. This cost-effective PACS solution enables health care professionals to access and examine patient records quickly and easily. Our ImageGrid™ PACS products easily integrate your existing electronic health records for optimized workflow.
Leverage our PACS solutions for simple setup, scalable DICOM storage, self-monitoring, multi-operation support, web-based system administration and other relevant features to elevate your operations and patient experience.
For more information about our ImageGrid™ PACS and other cost-effective medical data management solutions, contact us today. You can also reach out to one of our specialists to schedule a demo of our transformational products.
- Log in to post comments
